In a globalized business environment, organizations often collaborate with a network of vendors and suppliers to fulfill various operational needs. The Vendor Management Process Blade, a fundamental element of the Disciplined Agile framework, provides organizations with a structured approach to overseeing vendor relationships from identification to post-contract management. This article covers all that you need to know about vendor management, complete with how to effectively conduct it using the disciplined agile toolkit.
What Is Vendor Management?
Vendor Management Definition: Vendor management refers to the strategic practice of effectively collaborating with external partners, suppliers, and organizations to enhance various facets of an organization’s operations, offerings, and projects. This process blade encompasses strategies, practices, and guidelines to ensure that vendor interactions are streamlined, productive, and aligned with the organization’s goals and values.
It covers activities ranging from vendor selection and contract negotiation to ongoing collaboration and performance assessment. By following the Vendor Management Process Blade, organizations can optimize their vendor relationships, mitigate risks, and enhance the overall efficiency of their projects and operations.
What Is A Vendor In Project Management?
A vendor is an external organization or person that provides offerings that are of potential interest to your organization. They are also referred to as a supplier.
What Is The Purpose Of Vendor Management?
The aim of vendor management is to:
- Procure the right products and services from partner organizations
- Manage contracts and negotiate with partner organizations
- Oversee partnerships and maintain a steady increase in value of partnerships
- Address risks and impediments associated with partnerships
What Does Vendor Management Include?
The vendor management process blade includes the four views of the disciplined agile toolkit, i.e., Mindset, People, Flow, and Practices.
Within the mindset, there are eight philosophies that extend the Disciplined Agile Mindset. The Principles, Promises, and Guidelines within the disciplined agile mindset remain the same as for the entire disciplined agile toolkit. The People aspect addresses the roles and responsibilities that come under the vendor management process blade. Next, under the banner of Flow, is the workflow of vendor management that charts how vendor managers interact with other process blades within the disciplined agile framework. Further, the Practices include a goal-driven approach that indicates the process decision points you need to consider, a range of techniques or strategies for you to address each decision point, and the advantages and disadvantages of each technique. Let’s delve into all these views one by one in the forthcoming sections.
Disciplined Agile Philosophies for Effective Vendor Management:
-
Value through Collaborative Partnerships
Central to the DA mindset for vendor management is the unwavering focus on generating value through collaborative partnerships. Recognizing the power of collective expertise, organizations harness the strengths of external entities to enhance their offerings and operations.
-
Embracing Collaborative Partnerships
The pursuit of collaborative partnerships transcends traditional boundaries, even reaching across competitors. This mindset encourages organizations to seek alliances with both rivals and entities competing with each other, fostering an ecosystem of shared knowledge and innovation.
-
Nurturing Mutually Beneficial Relationships
Effective vendor management hinges on nurturing relationships that are mutually beneficial. By fostering transparent and symbiotic associations with suppliers and partners, organizations create an environment conducive to sustained growth and value creation.
-
Co-Creation Throughout the Lifecycle
The DA mindset advocates for co-creation throughout the entire vendor management lifecycle, spanning from procurement to implementation. This approach entails active participation of both internal experts and vendor specialists, ensuring that the collaboration is well-rounded and attuned to diverse perspectives.
-
Trust as Trusted Advisors
Within the organization, those practicing effective vendor management embody the role of trusted advisors. They offer valuable insights and guidance not only to the organization itself but also to suppliers and partners, aligning interests and facilitating informed decision-making.
-
Prioritizing Organizational Outcomes
In the pursuit of effective vendor management, organizational outcomes take precedence over localized process conveniences. In addition, operating with an enterprise-aware approach, decisions are made in consideration of the broader organizational context.
-
Fiduciary Responsibility to Protect
Acknowledging the weight of responsibility, effective vendor management practitioners embrace a fiduciary duty to safeguard the organization’s interests. As a result, this commitment ensures that actions taken align with the organization’s long-term goals and sustainability.
-
Holistic Risk Addressing
The DA mindset encourages a comprehensive approach to risk management. Proactively identifying and addressing risks in a holistic manner ensures that potential disruptions are minimized, fostering a resilient vendor management strategy.
Roles Under Vendor Management Process Blade:
-
Vendor Manager
The role of a vendor manager is pivotal in fostering and sustaining relationships between your organization and its vendors and partners. This includes the critical tasks of negotiating contracts, establishing standardized procedures for vendors, and identifying the most suitable vendors for your needs. Vendor managers not only cultivate these relationships but also assume fiduciary responsibility and hold signing authority on behalf of your organization. In certain cases, vendor managers might delegate signing authority to others, possibly with specific signing limits and scope to ensure prudent decision-making.
-
Procurement Manager
Within the vendor management landscape, the procurement manager stands as a key figure, steering the procurement team towards success. This role shoulders the overall responsibility of overseeing the procurement process. This includes everything from the initial requisition stage to the meticulous selection of vendors, skillful negotiation, and the crucial task of overseeing invoice payment. The procurement manager plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the procurement process is executed smoothly and aligns with the organization’s objectives.
-
Procurement Specialist
The role of procurement specialists is characterized by a diverse range of responsibilities aimed at optimizing the procurement process. These specialists engage in tasks such as analyzing the organization’s procurement needs and objectives, conducting market research to assess potential options, evaluating the cost structure of vendor proposals, and overseeing the successful fulfillment of agreements. In larger organizations, procurement specialists may specialize further by focusing on specific service or product categories or geographical locales. Reporting to the procurement manager, they might also be referred to as Purchasing Agents or Purchasing Clerks.
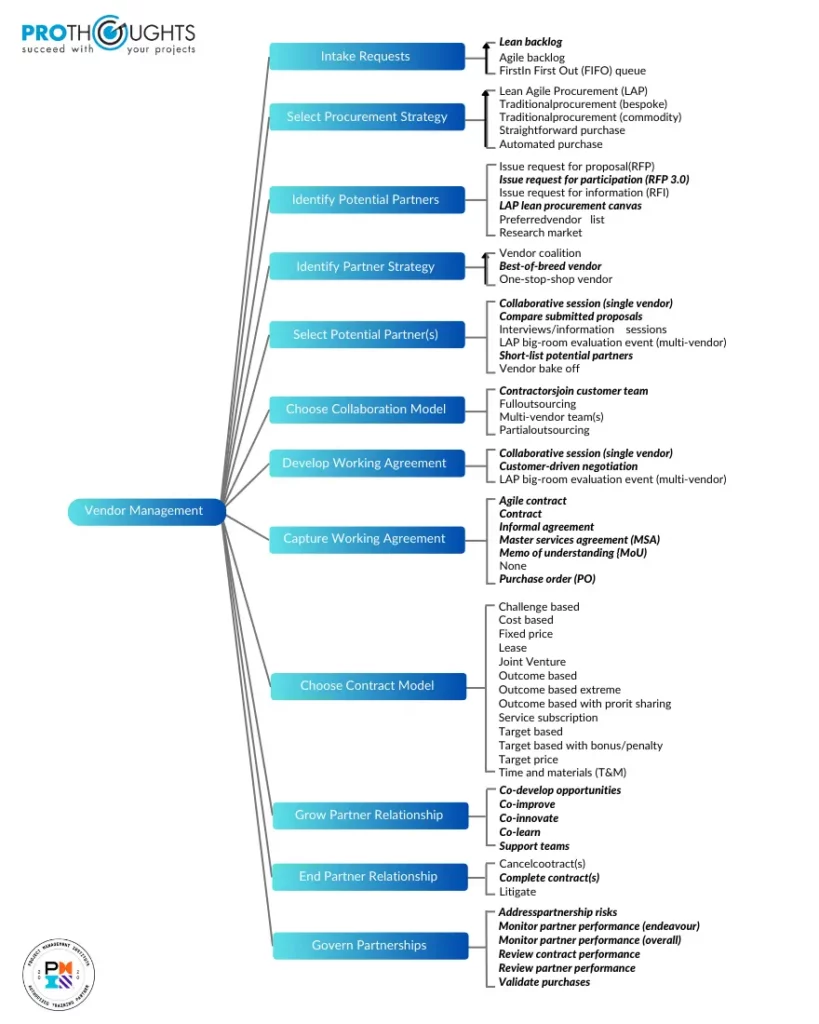
How To Handle Vendor Management? – Vendor Management Decision Points
Disciplined agile makes vendor management much simpler with a series of pivotal decision points that orchestrate the entire process. These are also termed vendor management practices. As shown in the image below, vendor management practices involve a wide range of decision points.
These decision points guide how your organization handles vendor interactions and procurement. Let’s delve into these decision points to gain a better understanding.
-
Intake Requests
At the core of vendor management lies the process of intake requests. Your vendor management team receives requests from stakeholders, examines their viability, and prioritizes them for action. If deemed ready, these requests are added to the team’s work backlog. Moreover, the appropriateness of requests hinges on factors like detail level, assessed by the team.
-
Select Procurement Strategy
Secondly, choosing the right procurement approach is crucial. This decision revolves around the nature of potential offerings. Simple, low-risk purchases may grant staff discretionary power, whereas more complex acquisitions might align with traditional methods. Moreover, agile strategies could be reserved for intricate purchases. Therefore, context plays a pivotal role in this choice.
-
Identify Potential Partners
The identification of potential partners involves determining who can provide the desired offerings, be it products or services. Complexity and uniqueness of offerings, coupled with existing partner capabilities, shape this decision. It’s about finding partners whose strengths align with your needs.
-
Identify Partner Strategy
Defining how you identify potential partners is equally important. This strategic choice rests on whether you seek extensive offerings from large vendors or specialized expertise from smaller ones. Your approach shapes the landscape of potential collaborations.
-
Select Potential Partners
Your strategy to select potential partners has far-reaching consequences. It influences your compatibility with partners and sets the tone for future interactions. Hence, you could say that the right strategy ensures a strong foundation for the partnership.
-
Choose Collaboration Model
Another key point is choosing a collaboration model. Collaboration models define how you work with partners. These models, therefore, outline how agreements are fulfilled and lay the groundwork for successful collaboration.
-
Develop Working Agreement
Crafting working agreements involves strategic decision-making. Whether through collaborative efforts or formal negotiations, the chosen approach shapes the trajectory of your partnership. It establishes the dynamics between you and your partner.
-
Capture Working Agreement
Documenting agreements is essential, especially as risk increases. The more comprehensive the documentation, the more secure your partnership becomes. Clarity in documentation is a safeguard against potential conflicts.
-
Choose Contract Model
Payment approaches significantly influence behavior. The contract model you choose motivates your behavior during collaboration and encourages the evolution of your partnership over time.
-
Grow Partner Relationship
Sustainable partnerships require nurturing. Your approach to growth dictates whether your relationship remains transactional or evolves into a mutually beneficial collaboration.
-
End Partner Relationship
Partnerships have lifecycles. Moreover, deciding how to end them is critical. Therefore, employing appropriate strategies ensures a graceful conclusion to the partnership.
-
Govern Partnerships
As a matter of fact, effective governance of partnerships is paramount. Ensuring received value, adherence to expectations, and proactive risk management collectively contribute to a successful partnership.
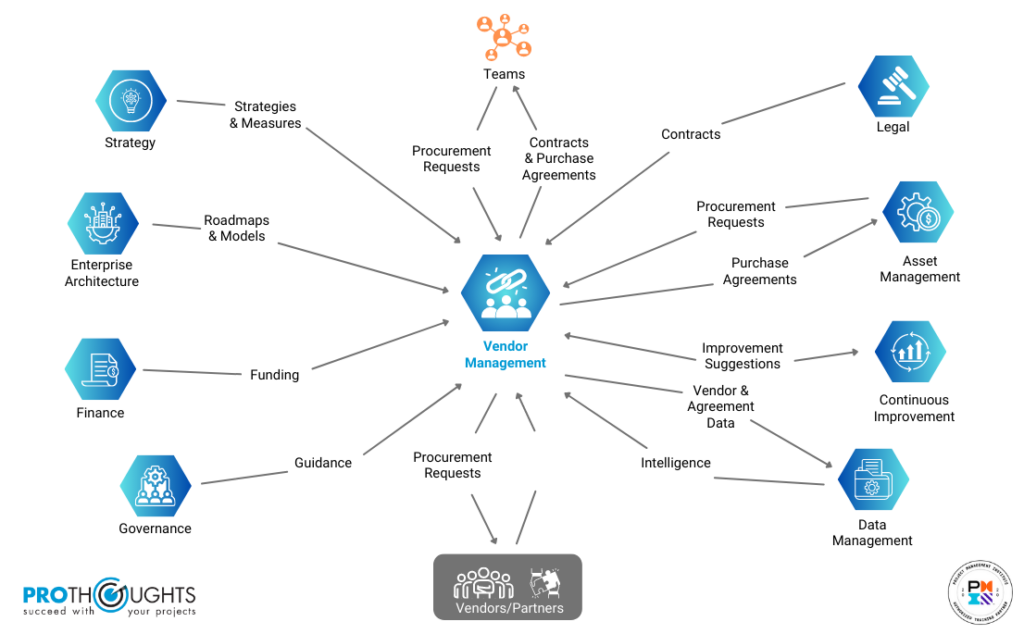
What Is The Role Of Vendor Management? – Vendor Management Workflows
Vendor management holds a critical position within any organization, contributing significantly to the orchestration of its operational processes. At a broader level, vendor management’s engagement can be visualized through the high-level workflow depicted in the figure. As shown below, the image underlines the intricate relationship between vendor management efforts and their seamless collaboration with different teams to effectively engage with vendors.
How To Improve Vendor Management? – Vendor Management Strategies
Effective vendor management is a cornerstone of organizational success, and employing the right strategies can significantly enhance this process within the Disciplined Agile framework. Here, we delve into strategies that align with a Disciplined Agile approach to optimize interactions with partners.
-
Collaborate with Stakeholders
Empower your vendor management team by actively engaging with stakeholders who require products or services. Their insights often hold valuable information on optimal options and the best-fit solutions. Therefore, by involving them upfront in the procurement process, you establish a collaborative environment built on trust and harness their domain expertise.
-
Diversify Vendor Relationships
Rather than limiting vendor partnerships for the sake of simplicity, aim for a diversified approach. A range of vendors brings a spectrum of capabilities to the table. Larger companies provide standardized offerings, sometimes willing to learn and adapt through collaboration. Smaller firms offer leading-edge expertise, while independent contractors contribute niche skills. This diversity allows you to tap into specialized strengths for different requirements.
-
Cultivate Partnerships
Recognize the significance of vendor staff in your value stream. Integrate them closely by treating them as integral members. In addition to this, strive for a seamless blend of full-time employees (FTEs), contractors, and vendors, erasing the lines between organizations. Therefore, this integration enhances collaboration and ensures a shared focus on project success.
The following additional strategies lead to more effective contracting:
-
Flexible Contracts
Contracts should reflect the context and nature of the engagement. Consider context-sensitive contracts that suit the scope of the endeavor. Tailor contracts for agile services to accommodate agile methodologies and similarly for traditional services. Context-aware contracts provide clarity and alignment, making them more effective.
-
Optimal Vendor Selection
Avoid extremes when evaluating vendors based on cost. Middle-ground vendors often strike the balance between quality and cost-effectiveness. The lowest bidders might compromise quality, while the highest may not align with your organization’s objectives. The middle path frequently offers the best value.
-
Embrace Flexible Funding
Prioritize flexible funding contracts over fixed-bid arrangements. Fixed-bid contracts can lead to a focus on initial price, often overlooking long-term value. Moreover, embrace a systems thinking approach, aiming to minimize total cost and maximize net value. Also, flexible funding contracts promote a holistic perspective.
-
Incremental Delivery Contracts
Mitigate risk through incremental delivery contracts. Breaking down large contracts into smaller, incremental deliverables reduces the overall risk associated with extensive projects. This approach, therefore, enhances transparency, allows for learning, and provides opportunities for strategic adjustments.
-
Outcome-Based Contracts
Align contracts with outcomes rather than features. Embrace an outcome-focused approach, that mirrors your organization’s internal metrics. In addition, define contracts in terms of customer-centric outcomes like increased sales, customer retention, or growth. Consequently, this ensures that the contracts are aligned with actual value.
-
Simplify Contractual Processes
Steer clear of overly detailed contractual processes. Extensive upfront planning can increase complexity and risk. Instead, opt for a streamlined approach that favors transparency and flexibility. Simplified processes encourage fairness and transparency, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
-
Monitor Fulfillment
Regularly monitor contract fulfillment and performance. Evaluating past performance guides future decisions on awarding new work to vendors. Utilize retrospectives to identify areas for improvement, enhancing the overall vendor partnership and project success.
You can learn all of these strategies in detail with our disciplined agile certification training. In this course, our expert instructors will walk you through all the best practices of vendor management so that you learn to manage stakeholders more effectively.
Why Is Vendor Management Essential For Your Organization?
-
The Growing Complexity and Competition
The business world is undergoing a profound transformation driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and global interconnectedness. These changes bring about not only a level of complexity but also competition. As a result, organizations can no longer effectively navigate on their own. From supply chain intricacies to evolving regulatory landscapes, businesses are confronted with a multitude of challenges that necessitate a collaborative approach.
-
Mitigating Risks Effectively
Vendor management emerges as a crucial solution to mitigate overall risk effectively. It empowers organizations to navigate this landscape by employing several risk-reduction strategies. Firstly, the inclusion of skilled contractors or outsourcing to proficient external entities addresses risks stemming from skill and capacity limitations. Secondly, collaborative partnerships spread the risk associated with novel ventures across multiple organizations. Although inherent risks exist in such collaborations, these can be managed through adept governance strategies and embracing the Disciplined Agile (DA) mindset for vendor management. Thirdly, the acquisition of significant or specialized items through sourcing specialists diminishes the risk of ill-suited purchases.
-
Delivering More, Delivering Faster
The collaboration facilitated by vendor management extends an organization’s capacity to deliver value to its customers. By leveraging the expertise and resources of external partners, businesses can accelerate the development and delivery of new or enhanced offerings. This speed-to-market not only meets customer demands but also strengthens the organization’s competitive edge.
-
Expanding Market Reach and Impact
Vendor management isn’t limited to mere transactional relationships; it extends to strategic partnerships that enable the creation of more robust offerings. Whether through customer-supplier relationships or true partnering arrangements, organizations can expand their value streams. This expansion could involve diversifying product lines, introducing complementary services, or tapping into new markets.
Conclusion
The Vendor Management Process Blade within the Disciplined Agile framework provides organizations with a comprehensive approach to effectively manage vendor relationships. In conclusion, we would like to say that by identifying vendors strategically, nurturing partnerships, and aligning vendor practices with agile principles, businesses can achieve improved collaboration, risk management, and cost optimization.